the heart of car: The engine
The chain of reactions which achieve that objective is set in motion by a spark, which ignites a mixture of petrol vapour and compressed air inside a momentarily sealed cylinder and causes it to burn rapidly. This is why the machine is called internal combustion engine. As mixture combustion to extend it, so that you can provide electric cars.
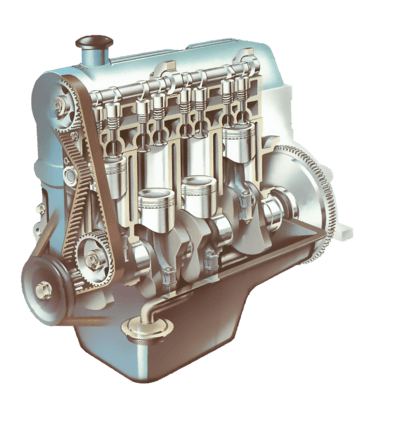
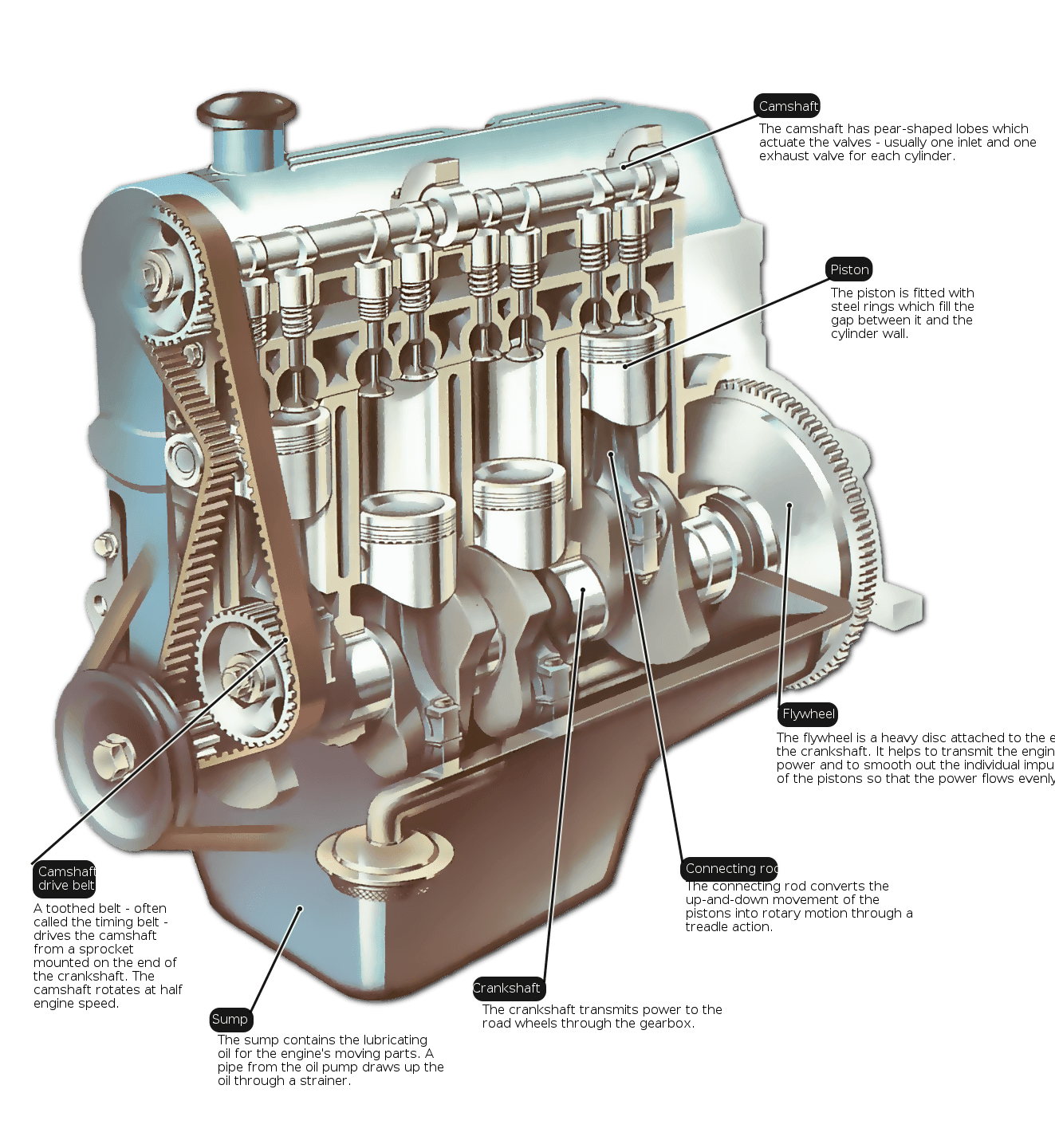
Engine must have a strong structure to withstand the heavy workload. It consists of two basic parts: the lower, heavier section is the cylinder block, a casing for the engine’s main moving parts; the detachable upper cover is the cylinder head.
The cylinder head contains valve-controlled passages through which the air and fuel mixture enters the cylinders, and the other is through their burning gas to discharge.
The block houses the crankshaft that converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion at the crankshaft. Often the block also houses the camshaft, which operates mechanisms that open and close the valves in the cylinder head. Sometimes the camshaft is in the head or mounted above it.

One of the most common engine that includes four continuous vertical cylinder. This is known as an in-line engine. Cars with capacities exceeding 2,000cc often have six cylinders in line.
The more compact V-engine is fitted in some cars, especially vehicles with eight or 12 cylinders, and also some with six cylinders. Here the cylinders are arranged opposite each other at an angle of up to 90 degrees.
Some engines have horizontally opposed cylinders. They are an extension of the V-engine, the angle having been widened to 180 degrees. Advantage is that can be balance in some way.
The cylinders in which the pistons operate are cast into the block, as are mountings for ancillary equipment such as a filter for the oil which lubricates the engine, and a pump for the fuel. An oil reservoir, called the sump, is bolted underneath the crankcase.
Both block and head are usually made of cast iron. Because it can be lighter and more effectively dissipate heat, so generally choose aluminum head.