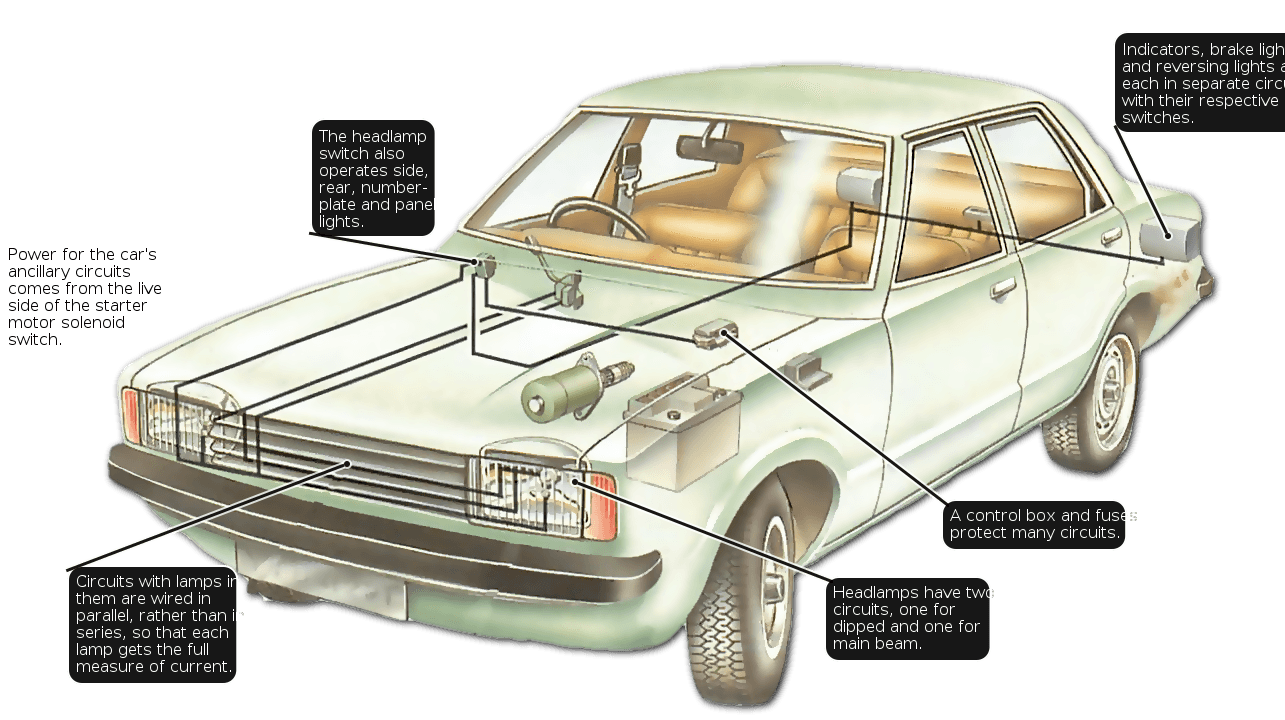
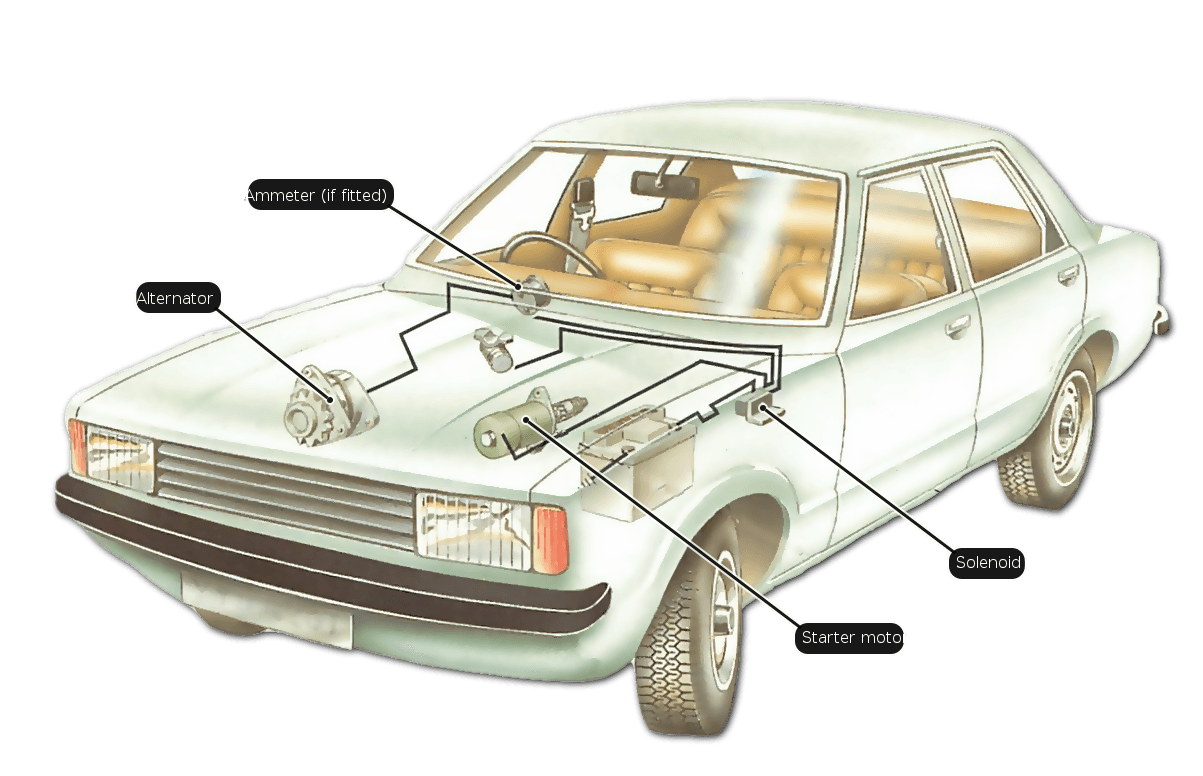
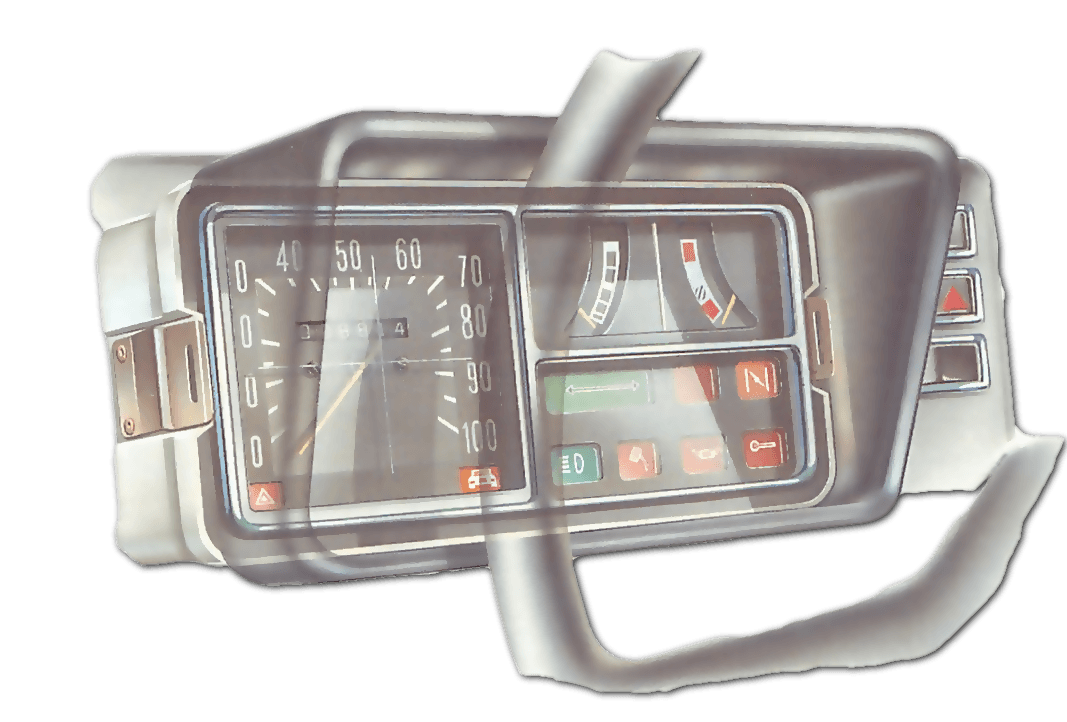
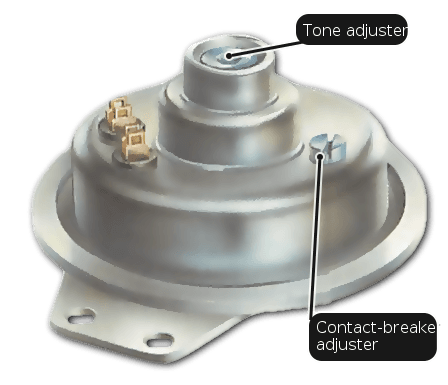
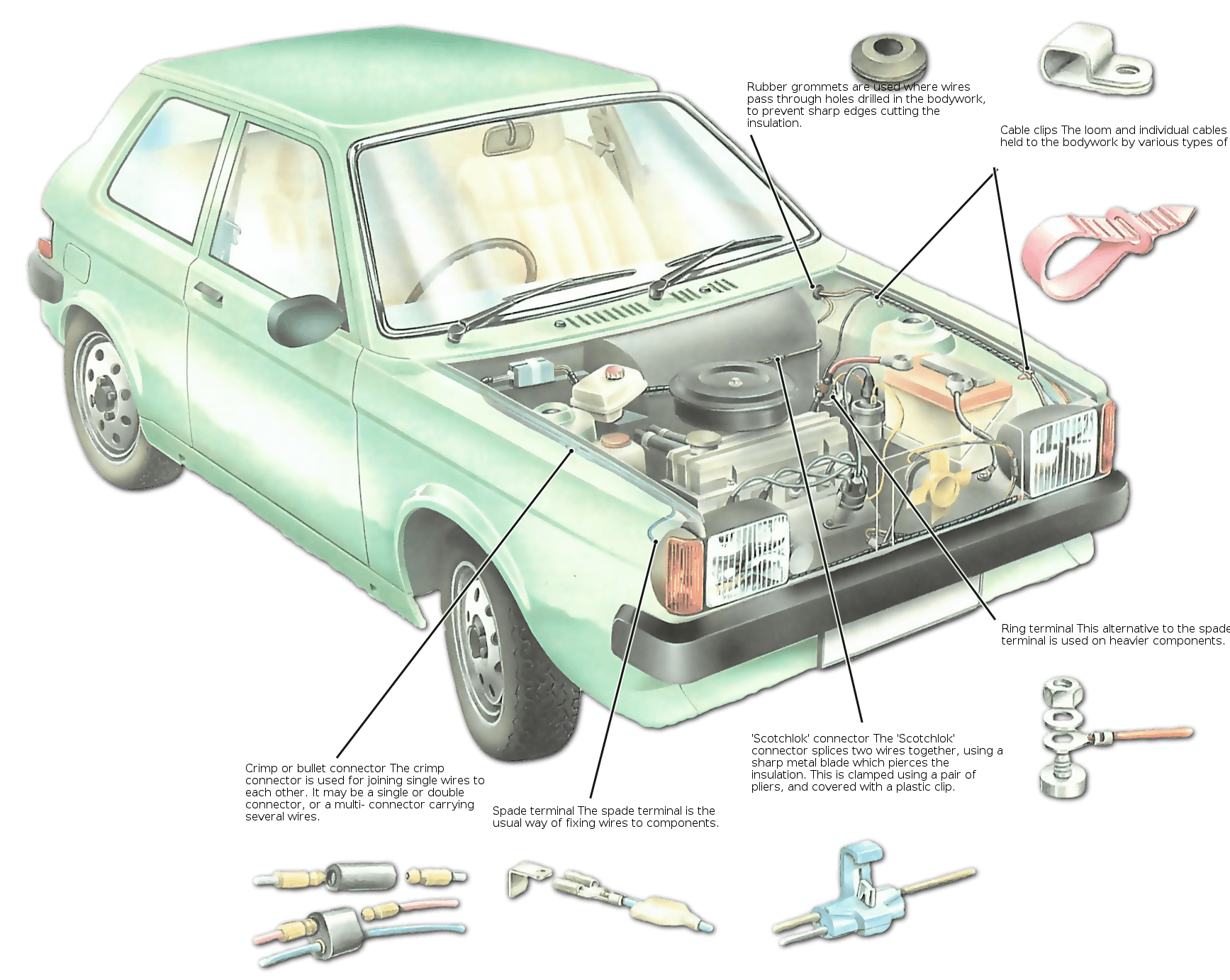
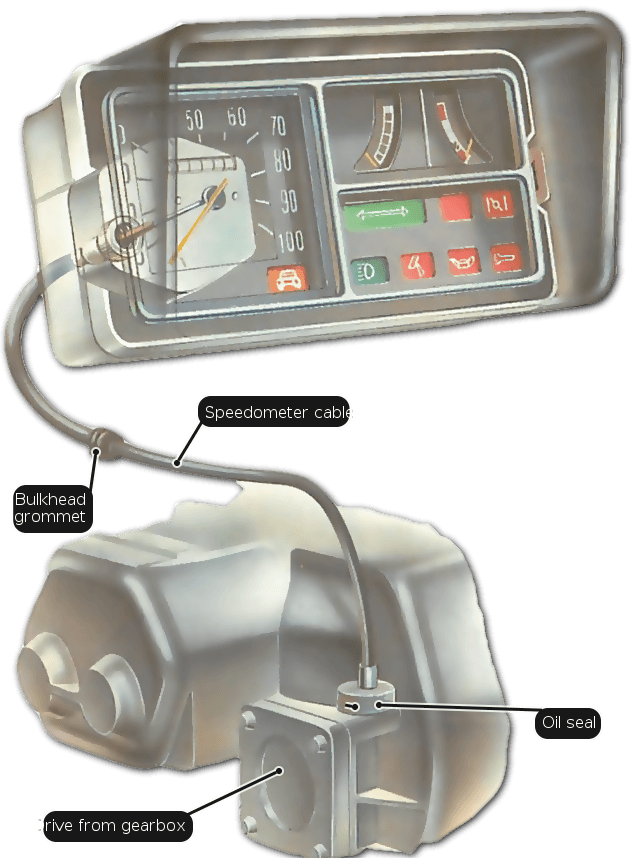
How to align headlights at home
Chalk a vertical line on the wall or the garage doors, opposite the centre of the car bonnet. Draw two outer lines equidistant from the centre line and the same distance apart as the headlamp centres. Drive the car close to the wall, facing it at right-angles. Bounce the car to settle the suspension, then chalk a vertical line on the wall opposite the centre of the car. Measure the distance between the headlamp centres, halve this figure and draw two more vertical lines at the same distance on each…
Read More