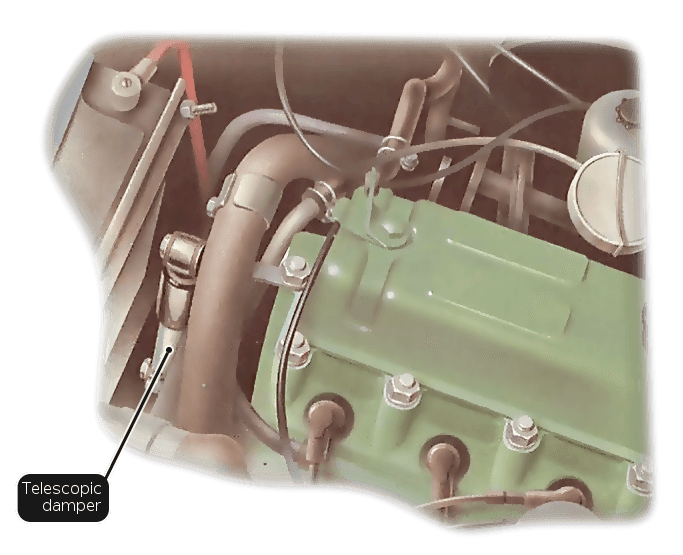
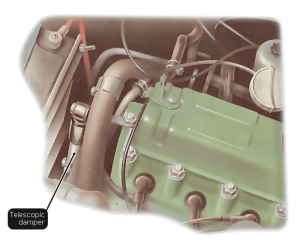
How to check the engine damper
The engine is easy to rock rubber parts, especially at idle speed, with excess damper or pure bars combined with rubber shrubs held at both ends of the stabilizer.
The car is transverse to the engine, and several others, the damper – either a purely stable bar, a hydraulically retractable unit or a combination of both.
Types of engine damper
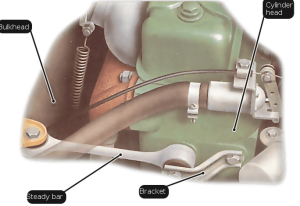
There may be one or two dampers, usually mounted between the cylinder brackets and the other in the bulkhead.
The damper is also sometimes mounted from the engine block or the oil pan to the mounting brackets on the front chassis or subframe of the crossbeam.
The damper may be a stabilized bar – a steel drawbar with rubber tired eyes at both ends or a telescopic hydraulic damper.
Check the damper main service period, every 12,000 miles (20,000 km), or if you suspect the engine is abnormal. This may appear as a sound acceleration or braking, sometimes accompanied by excessive movement of the shift lever.
Check for distortion of the bushes, softness, death, cracking or oil contamination.
Try moving the bar by hand or lever. If it moves, one or two shrubs may be wrong.
Remove the bar and adapt to the new bushes. In some car bushes you have to replace the entire bar.
Open both ends of the bar and delete it. Check the bars and bolts and mount points to make sure they are not damaged, bent or rusted out. Replace any doubtful parts.
Alternative shrubs are usually a simple embedded health. Early mini-skirt metal cone fitted into the bushes: News These are easily retrofitted with the deputy bar.
You may need to tighten the bolts in the rod position when changing the bar. Check the telescopic damping in the same way, but also look for signs of hydraulic leaks.
If you find a faulty damper, check other engine over-motion accessories to make sure there is no damage.
Check whether the accessories also soften, crack, die or separate rubber-to-metal bonds.
Replacing steady bar bushes
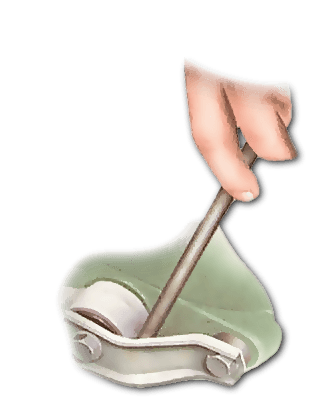
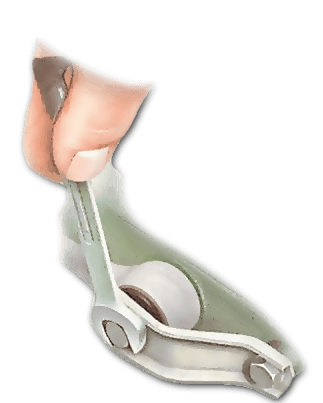
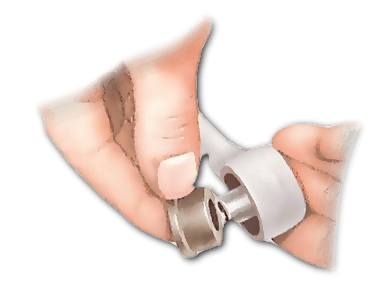
When you Open the bonnet, you should remove any components that are in the way. Wipe the bar, its bushes and the mountings clean. Inspect the bushes by levering them upwards, this will reveal any cracks or deterioration in the rubber. Any excessive movement either upwards or sideways suggests a faulty bush. Renew as necessary.
Checking adjustable steady bars
This stable bar can not be removed by adjusting it: first loosen the locknut.
The stable bar is adjustable in length. Adjust the lever until there is no pressure when the engine is in the normal position.
If the stabilizer bar is adjusted too long or short, this will give a constant rubber bush.
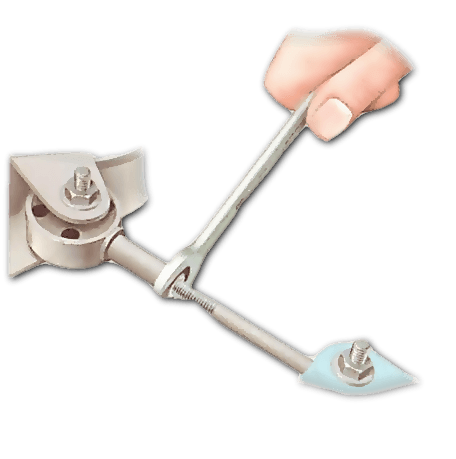

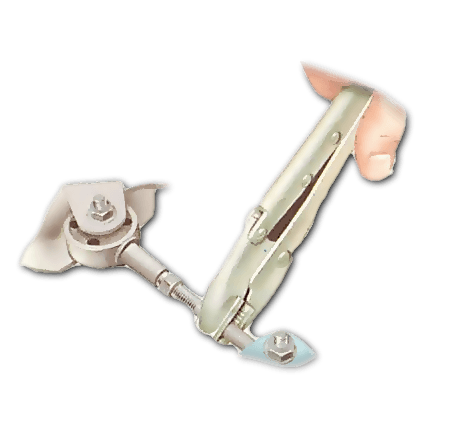
Hold the bar self-locking control and rotate it.
After adjustment should be possible to just move the bar tension in the bushes. The car’s maintenance manual will give a maximum and minimum length.
If you need to adjust it outside of this range, the engine accessory may be distorted or perish.
You can adjust the number of bars in place to loosen the locknut, put the bar; others are the rough end.
When you tighten the locknut, take care that you do not twist the shrub.
Checking a telescopic damper

If you have any reason to suspect that a telescopic damper dampers properly, it either weakens or has caught the solid – or if you suspect it has leaked, remove it and test the suspension in the same suspension.
If a damper is suspected, replace it. Gripping the damper will become apparent as excessive vibration is transmitted to the body.